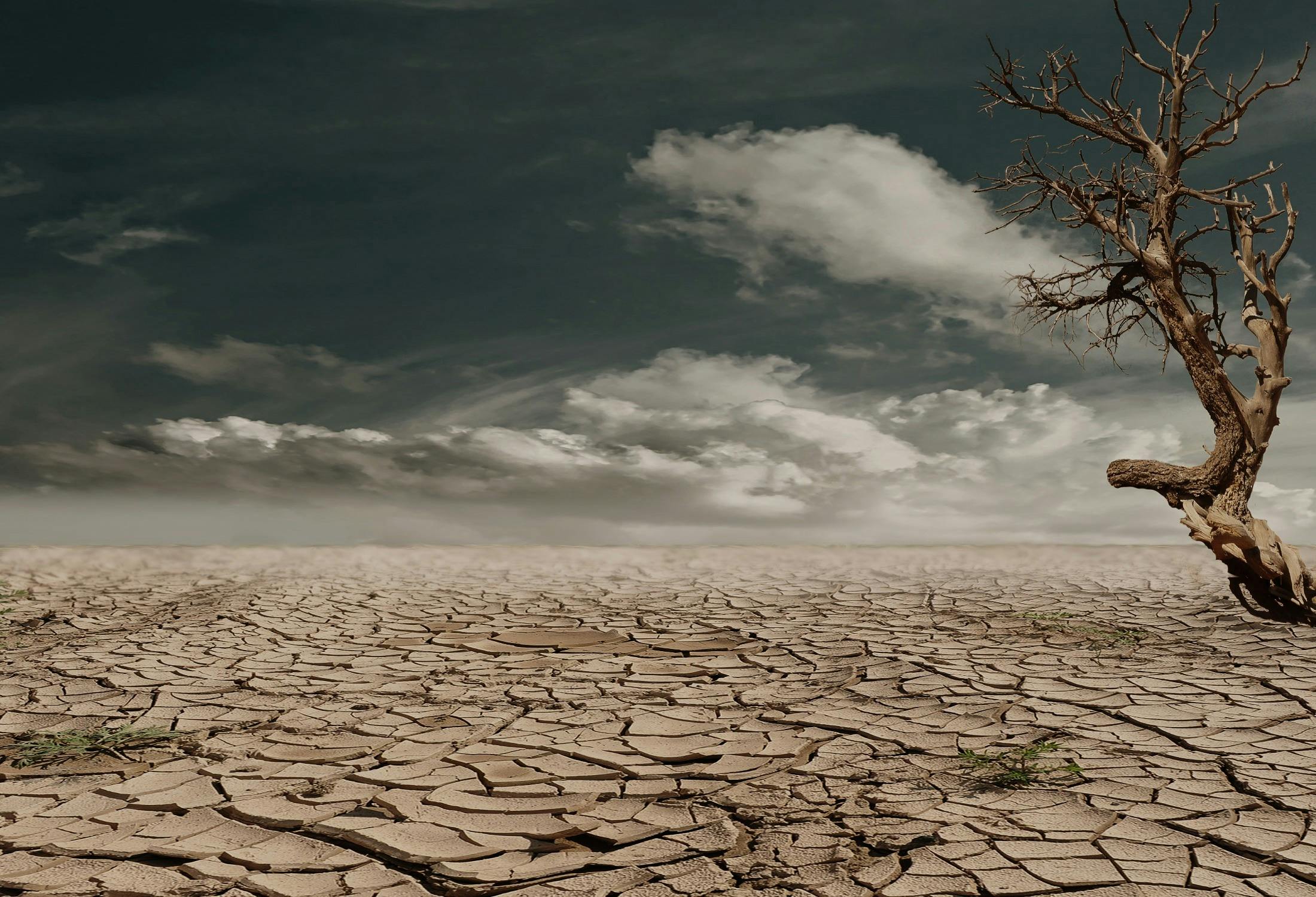
The world is facing a profound environmental crisis, as the devastating effects of climate change continue to impact wildlife populations across the globe. This comprehensive article explores the alarming consequences of this phenomenon, including biodiversity loss, habitat destruction, and the extinction of countless species. It delves into the cascading effects on ecological balance, the vital importance of conservation efforts, and the urgent need for sustainable practices to mitigate these environmental challenges.
Drawing from extensive scientific research and real-world examples, this in-depth exploration provides a holistic understanding of the climate crisis and its far-reaching implications for the natural world. By shedding light on the global warming effects and the relentless environmental degradation that threatens the very fabric of our ecosystems, the article highlights the crucial steps being taken to protect and preserve vulnerable species and their habitats, ultimately fostering ecosystem resilience in the face of this unfolding crisis.
Key Takeaways
- Climate change has devastated wildlife populations, leading to alarming rates of biodiversity loss and habitat destruction.
- The disruption of ecological balance due to species extinction has far-reaching consequences for the natural world.
- Conservation efforts and sustainable practices are crucial in mitigating the effects of the climate crisis on wildlife.
- Protecting vulnerable species and restoring ecosystem resilience are essential to preserving the delicate balance of our planet.
- Urgent action is needed at global, national, and individual levels to address the environmental degradation caused by climate change.
Introduction to Climate Change and Wildlife
As the global climate continues to shift due to human-induced activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, the impacts on the natural world are becoming increasingly severe and far-reaching. At the heart of this environmental crisis lies the critical issue of climate change, a phenomenon that is reshaping the delicate balance of ecosystems and threatening the very existence of countless species across the globe.
What is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to the long-term changes in global or regional weather patterns, driven primarily by the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, trap heat from the sun, causing the Earth’s temperature to rise over time. This warming trend, often referred to as global warming, is altering temperature and precipitation patterns, leading to dramatic changes in the natural habitats and life cycles of wildlife.
The Importance of Biodiversity
At the heart of this environmental crisis is the critical issue of biodiversity, the vast array of plant and animal species that make up the intricate web of life on our planet. Biodiversity plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystem functions, from regulating the climate and purifying water to providing food and shelter for countless species. However, as climate change disrupts these natural systems, the loss of biodiversity is accelerating at an alarming rate, with devastating consequences for the overall health and resilience of the natural world.
Climate Change and Habitat Destruction
The devastating effects of climate change extend far beyond the warming of the planet. One of the most alarming consequences is the habitat loss and deforestation that are rapidly transforming the natural landscapes that wildlife call home. As temperatures rise and precipitation patterns shift, the delicate balance of ecosystems is being disrupted, leading to ecosystem fragmentation and land use changes that are pushing many species to the brink of survival.
The impact of climate change on wildlife habitats is multifaceted and far-reaching. Rising sea levels and increased frequency of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires, are causing the degradation and destruction of vital natural habitats. Fragile ecosystems like coral reefs, coastal wetlands, and tropical rainforests are particularly vulnerable, as they struggle to adapt to the rapid environmental changes.
Alongside the climatic factors, human activities such as deforestation, urban expansion, and unsustainable agricultural practices are further exacerbating the habitat loss and ecosystem fragmentation that wildlife face. The conversion of natural habitats into farmland, residential areas, and infrastructure projects is eroding the essential living spaces and migration corridors that many species depend on for their survival.
As habitats become increasingly fragmented and degraded, wildlife populations are forced to adapt or relocate, often leading to increased competition for limited resources and disruptions to established food webs. This domino effect can have devastating consequences for the overall health and resilience of ecosystems, putting numerous species at risk of extinction.
Addressing the crisis of habitat loss and deforestation is a crucial component of the fight against climate change and the preservation of biodiversity. Comprehensive conservation efforts, sustainable land use practices, and the restoration of degraded habitats are vital in ensuring the long-term survival of the planet’s diverse array of wildlife.

Impact of Global Warming on Species
As the planet’s temperature continues to rise due to global warming, the effects on wildlife are becoming increasingly severe. Species around the world are facing the challenge of adapting to these dramatic environmental changes, often with devastating consequences.
Rising Temperatures and Species Adaptation
Many species, unable to keep pace with the rapid shifts in their habitats, are struggling to adapt to the higher temperatures and altered weather patterns. Some are forced to migrate to new areas in search of more suitable conditions, while others face the threat of local extinction as their natural habitats become inhospitable.
Shifting Habitats and Migration Patterns
The shifting of habitats and disruption of established migration routes is a major concern for wildlife. As global warming alters the landscape, species must adapt by moving to new areas, often encountering barriers or encountering difficulties in accessing essential resources along the way. This can lead to a breakdown in the delicate balance of food webs and ecosystem functions.
Food Chain Disruptions
The cascading effects of global warming on wildlife can also disrupt the intricate food chains that sustain entire ecosystems. The loss or displacement of key species can have a domino effect, leading to imbalances in prey-predator relationships, the availability of food sources, and the overall resilience of the natural world.
| Impact of Global Warming on Wildlife | Example | Consequences |
| Rising Temperatures | Polar bears struggling to find food due to melting sea ice | Declining population and increased risk of extinction |
| Habitat Shifts | Migratory birds unable to reach traditional breeding grounds | Disruption of breeding cycles and population decline |
| Food Chain Disruption | Collapse of coral reef ecosystems due to ocean acidification | Loss of biodiversity and destabilization of marine food webs |
Biodiversity Loss and Ecological Imbalance
The alarming issue of biodiversity loss is at the heart of the ongoing environmental crisis, with the cascading effects resulting in a dangerous ecological imbalance. As climate change and human activities continue to threaten the delicate balance of nature, the number of endangered and extinct species has been steadily rising, compromising the overall health and resilience of the natural world.
Endangered and Extinct Species
The impact of global warming and human interference on wildlife habitats has led to a dire situation for many species, with countless flora and fauna now classified as endangered or even extinct. From the iconic polar bears struggling to adapt to melting Arctic ice to the Sumatran rhinos facing habitat destruction, the list of threatened species continues to grow at an alarming rate. This biodiversity loss not only diminishes the richness and beauty of our planet but also disrupts the intricate web of life that sustains entire ecosystems.
Ecosystem Disruptions
As the number of endangered and extinct species rises, the delicate balance of ecosystems is being severely compromised. The loss of keystone species, essential for maintaining the structure and function of their habitats, can trigger a cascading effect that ripples through the entire food chain. This ecosystem disruption can lead to the collapse of entire systems, jeopardizing the survival of countless other species and compromising the overall ecological imbalance. The consequences of these disruptions can be far-reaching, affecting everything from the availability of natural resources to the resilience of communities in the face of environmental challenges.
| Endangered Species | Ecosystem Disruptions |
| Polar bearsSumatran rhinosBlack-footed ferretsVaquita porpoisesMountain gorillas | Collapse of food chainsDisruption of natural resource availabilityIncreased vulnerability to environmental challengesLoss of ecosystem resilienceCascading effects on dependent species |
Climate Change on Wildlife
As the world grapples with the escalating impacts of climate change, its far-reaching effects on various forms of wildlife have become increasingly apparent. From terrestrial wildlife to marine wildlife and avian wildlife, the changing environmental conditions driven by global warming are posing unprecedented challenges to the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Terrestrial Wildlife
Terrestrial wildlife, including iconic species like tigers, elephants, and polar bears, are facing significant habitat loss and disruptions to their migration patterns as a result of climate change. Rising temperatures, shifting precipitation patterns, and the increased frequency of extreme weather events are altering the landscapes they have long relied upon, forcing them to adapt or perish. The fragmentation and degradation of their natural habitats, often exacerbated by human activities such as deforestation, further compound the difficulties these species face in finding suitable living conditions.
Marine Wildlife
The impacts of climate change on marine wildlife are equally alarming. Warming ocean temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in currents and nutrient availability are affecting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. Species like coral reefs, sea turtles, and whales are struggling to survive as their habitats are transformed, and their food sources become scarce or unpredictable. The melting of Arctic sea ice, in particular, poses a grave threat to numerous marine wildlife species that rely on this critical habitat for their survival.
Avian Wildlife
The avian wildlife of our planet is also facing significant challenges due to climate change. Migratory bird species are experiencing disruptions to their migration patterns, with some arriving at their breeding grounds too early or too late, leading to mismatches with the availability of food and other resources. Additionally, the increased frequency of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and droughts, can devastate bird populations, affecting their nesting habits, food sources, and overall survival rates.
The cascading effects of climate change on these diverse forms of wildlife are undeniable and often intertwined. As habitats are lost, food chains are disrupted, and migration patterns are altered, the overall resilience and stability of ecosystems are severely compromised. Understanding and addressing the complex, multifaceted impacts of climate change on terrestrial wildlife, marine wildlife, and avian wildlife is crucial in our efforts to protect and preserve the rich biodiversity of our planet.
Environmental Degradation and Ecosystem Resilience
As the climate crisis continues to escalate, the issue of environmental degradation has become increasingly pressing, with far-reaching consequences for the resilience of our planet’s ecosystems. Two critical factors contributing to this alarming trend are the ongoing deforestation and habitat fragmentation that are devastating wildlife habitats around the world.
Deforestation and Habitat Fragmentation
The relentless clearing of forests for agriculture, urban development, and resource extraction has led to the destruction of critical habitats, forcing many species to struggle for survival in shrinking and isolated pockets of their former ranges. This habitat fragmentation not only disrupts the natural migration patterns and breeding cycles of animals but also compromises the overall ecosystem resilience, making it increasingly difficult for these delicate systems to recover from the impacts of climate change.
Pollution and Toxic Waste
Alongside the devastation caused by deforestation and habitat loss, the scourge of pollution and toxic waste continues to plague many ecosystems, further undermining their ability to adapt and recover. The introduction of harmful chemicals, plastics, and other pollutants into the environment can have catastrophic effects on wildlife, disrupting food chains, contaminating water sources, and causing long-term environmental degradation.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges will require a concerted global effort to not only mitigate the effects of climate change but also to restore and protect the natural habitats that are essential for the survival of countless species. Only by tackling the root causes of environmental degradation can we hope to build the resilience necessary to safeguard the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.

Conservation Efforts and Sustainable Practices
In the face of the climate change crisis, conservation efforts and sustainable practices have become crucial to protecting wildlife and their habitats. One of the primary strategies employed is the establishment of protected areas and wildlife reserves, which aim to safeguard vulnerable species and their ecosystems from the devastating effects of global warming.
Protected Areas and Wildlife Reserves
These designated conservation zones provide a haven for endangered species, allowing them to thrive free from the threats of habitat destruction, poaching, and human encroachment. By preserving these critical habitats, conservation efforts can help maintain the delicate balance of the natural world and ensure the survival of countless plant and animal species.
Reforestation and Habitat Restoration
Alongside the creation of protected areas, reforestation and habitat restoration efforts play a vital role in combating the climate crisis and its impact on wildlife. By replanting trees and restoring degraded ecosystems, these initiatives help to rebuild the essential carbon sinks and biomass that are crucial for regulating the Earth’s climate and providing suitable habitats for diverse species.
Renewable Energy and Emission Reductions
Transitioning to renewable energy sources and implementing strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are also crucial components of the conservation efforts to mitigate climate change. By moving away from fossil fuels and embracing clean, sustainable energy solutions, we can significantly reduce the human-induced factors that contribute to global warming, ultimately safeguarding the future of wildlife and their habitats.
Through a multifaceted approach that combines the establishment of protected areas, reforestation and habitat restoration, and the adoption of renewable energy, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient future for the natural world, where wildlife can thrive in the face of the ongoing climate crisis.
Global Collaboration and Policy Initiatives
Addressing the pressing issue of climate change and its devastating impact on wildlife requires a coordinated global effort. Governments, international organizations, and policymakers have recognized the urgency of the situation and have taken steps to establish international agreements and regulations aimed at mitigating the crisis and protecting biodiversity.
International Agreements and Regulations
The Paris Agreement, a landmark international treaty, has set ambitious goals to limit global temperature rise and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Similarly, the Convention on Biological Diversity has been a driving force in promoting global collaboration and implementing policy initiatives to safeguard endangered species and preserve fragile ecosystems. These agreements have laid the foundation for coordinated regulations and actions across nations, fostering a unified approach to tackling the climate change crisis.
Public Awareness and Education
Alongside these policy initiatives, the importance of public awareness and environmental education cannot be overstated. Engaging citizens, communities, and grassroots organizations in the fight against climate change and its impact on wildlife is crucial. By raising public awareness and providing environmental education, individuals can become empowered to adopt sustainable practices, support conservation efforts, and advocate for more robust policy initiatives and global collaboration to protect the natural world.
Role of Individuals and Communities
While governments and policymakers play a crucial role in addressing the climate change crisis, the actions of individuals and local communities can make a significant impact in protecting wildlife and the environment. By adopting eco-friendly lifestyle choices and engaging in grassroots activism, we all have the power to drive positive change and safeguard the natural world for generations to come.
Eco-friendly Lifestyle Choices
One of the most impactful ways individuals can contribute to the conservation of wildlife is by making sustainable choices in their daily lives. This includes reducing our carbon footprint by embracing renewable energy sources, such as solar power or wind energy, and supporting businesses that prioritize environmentally responsible practices. Additionally, we can make conscious decisions to minimize waste, conserve water, and adopt a more plant-based diet, all of which have a tangible effect on reducing our environmental impact.
Volunteering and Activism
Beyond personal lifestyle changes, individuals can also get actively involved in community-based conservation efforts and environmental advocacy. Volunteering with local organizations that work to restore habitats, protect endangered species, or raise awareness about the climate crisis can be a powerful way to contribute to the cause. Similarly, engaging in peaceful protests, writing to elected officials, or participating in community clean-up initiatives can amplify our collective voice and inspire meaningful change at the grassroots level. By embracing our role as environmental stewards, we can collectively work towards a more sustainable future for our planet and its wildlife.

FAQ
What is climate change and how does it impact wildlife?
Climate change refers to the long-term shift in global or regional climate patterns, primarily caused by human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. These changes can have devastating effects on wildlife, including habitat destruction, biodiversity loss, and species extinction. As temperatures rise, precipitation patterns shift, and extreme weather events become more frequent, many species struggle to adapt, leading to an ecological imbalance.
How does habitat destruction contribute to the climate crisis?
Habitat destruction, often driven by human activities like deforestation, urban expansion, and unsustainable land use practices, is a major contributor to the climate crisis. When natural habitats are degraded or lost, it not only forces wildlife to relocate or adapt, but it also removes important carbon sinks, such as forests, that help regulate the global climate. This creates a vicious cycle where habitat loss exacerbates climate change, which in turn leads to further habitat destruction.
What are the specific ways in which global warming is impacting different types of wildlife?
Global warming is affecting wildlife in various ways, including changes in species’ migration patterns, disruptions to food chains, and the forced relocation of habitats. Rising temperatures are causing some species to adapt or move to new areas, often leading to conflicts with other species or the inability to find suitable resources. Additionally, the shifting of habitats and the disruption of established ecosystems can have cascading effects on the overall health and stability of the natural world.
How is biodiversity loss connected to the ecological imbalance caused by climate change?
The loss of biodiversity, or the decline in the variety of living species, is a direct consequence of the ecological imbalance caused by climate change. As habitats are destroyed and species become endangered or extinct, the delicate web of interdependence that sustains ecosystems is disrupted. This can lead to cascading effects, such as food chain disruptions, the collapse of pollinator populations, and the overall compromising of the natural world’s resilience and ability to adapt to the ongoing climate crisis.
What are some of the conservation efforts and sustainable practices being implemented to mitigate the impact of climate change on wildlife?
Conservation efforts and sustainable practices are crucial in addressing the impact of climate change on wildlife. These include the establishment of protected areas and wildlife reserves, reforestation and habitat restoration initiatives, the transition to renewable energy sources, and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, global collaboration through international agreements and regulations, as well as public awareness and education, play a vital role in driving these efforts to protect the natural world.
How can individuals and communities contribute to the protection of wildlife in the face of the climate crisis?
Individuals and communities can play a significant role in addressing the climate change crisis and its impact on wildlife. Some key ways include making eco-friendly lifestyle choices, such as reducing carbon footprint, supporting sustainable businesses, and adopting renewable energy. Additionally, volunteering, activism, and participation in conservation efforts can help drive grassroots movements and inspire broader societal change to protect the natural world.